Ambulatory operations
Arthroscopy explainedArthroscopic operations are modern, minimally invasive operating techniques in which small fibre optics and video cameras are inserted into the joint through tiny incisions (0.2”). The necessary surgical procedure is carried out using miniature instruments and can be viewed on a video monitor. It is also known as ‘keyhole surgery’. The first arthroscopic meniscus operation was carried out in 1962. Since then arthroscopic operations have been gaining ground. Today, an arthroscopy can be performed on almost any joint. Advantages of the arthroscopy are minimal operation trauma, less operative risk and reduced treatment times and period of disability compared to open surgery.
|
Arthroscopies are mostly performed on knee joints. The operation usually necessitates a short-duration full anaesthetic or a spinal anaesthetic. Following insertion of the pencil-sized arthroscope the joint is filled with sterile irrigation fluid so that about half of the joint is visible and details can be closely examined. Structures in the knee such as meniscus, cartilage or ligaments can be investigated using special instruments. If the pre-operative diagnosis is confirmed the necessary procedure can be carried out during the arthroscopy. Torn menisci, ruptured ligaments, cartilage damage and many other ailments of the knee |


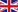


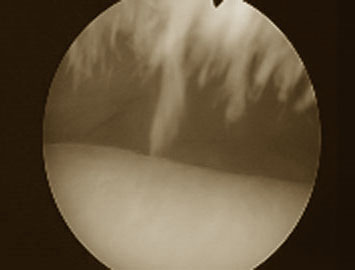 frayed articular cartilage of the knee
frayed articular cartilage of the knee damaged anterior cruciate ligament
damaged anterior cruciate ligament